Law of dilution
Wilhelm Ostwald’s dilution law is a relationship between the dissociation constant and the degree of dissociation of a weak electrolyte (acids, bases).
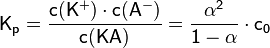
| Kp | constant of protolysis |
| α | degree of dissociation (or degree of protolysis) |
| c(A-) | concentrations of anions |
| c(K+) | concentration of cations |
| c0 | overall concentration |
| c(KA) | concentration of associated electrolyte |
Concerning conductivity, this results in the following relation:
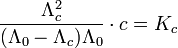
| Kc | constant of dissociation |
| Λc | equivalent conductivity |
| Λ0 | boundary conductivity |
| c | concentration of electrolyte |




